Feb 24,2026
Retention of Antioxidants
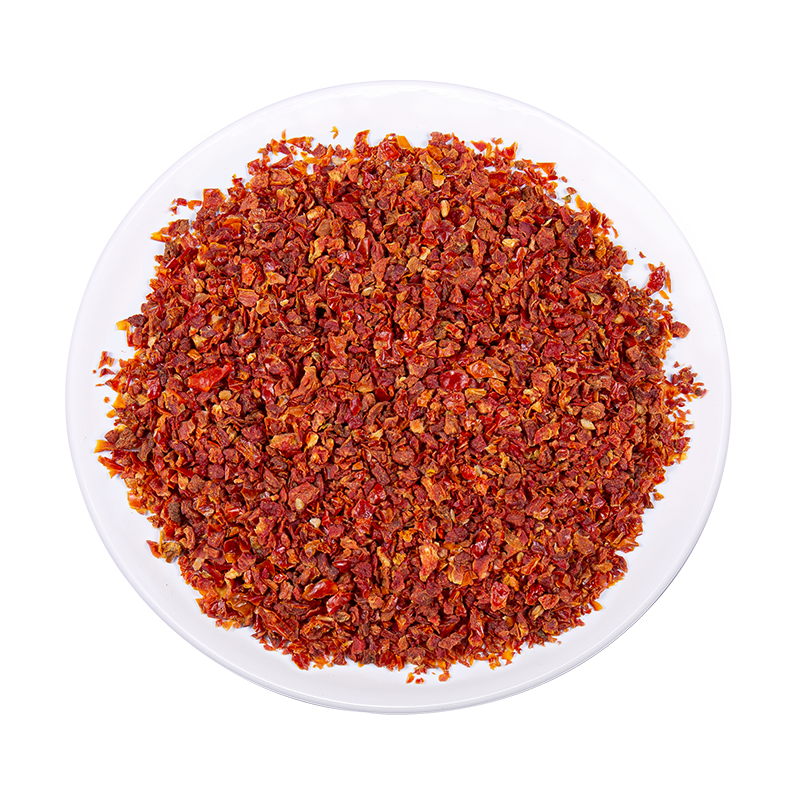
Dehydrated Red Pepper is naturally rich in antioxidants, including vitamin C, carotenoids such as beta-carotene and capsanthin, and flavonoids. These compounds help neutralize free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and supporting overall health. While the dehydration process involves heat, which can affect certain heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C, many of the carotenoids and polyphenols remain stable. Carotenoids, in particular, are highly resilient to heat and maintain their antioxidant activity, ensuring that dehydrated red pepper continues to deliver a substantial portion of the health-promoting compounds found in fresh peppers. This makes dehydrated red pepper a convenient and concentrated source of antioxidants that can be easily incorporated into daily diets or culinary applications.
Preservation of Nutritional Benefits
In addition to antioxidants, dehydrated red pepper retains a wide spectrum of other nutrients. The removal of water during the dehydration process naturally concentrates vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds per gram, meaning that the nutritional density of the pepper increases. Compounds such as capsaicin, responsible for the characteristic heat, remain largely intact and continue to provide documented health benefits, including enhancing metabolism, reducing inflammation, and supporting cardiovascular function. Moreover, essential minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and iron are preserved, making dehydrated red pepper not only a flavorful ingredient but also a nutrient-dense addition to meals. Its concentrated form allows for convenient use in cooking while maintaining the health benefits of fresh peppers.
Factors Affecting Health Benefits
The degree to which dehydrated red pepper retains its antioxidant and nutritional value depends on several factors.
Dehydration Temperature: High temperatures can accelerate the degradation of heat-sensitive compounds, such as vitamin C, but carotenoids and flavonoids tend to remain stable. Methods such as low-temperature drying or freeze-drying preserve nearly all antioxidants and bioactive compounds, producing a product that closely mirrors the nutritional profile of fresh peppers.
Exposure to Light and Air: Oxidation can occur if the dehydrated peppers are exposed to oxygen or UV light, which may reduce the potency of certain antioxidants. Using airtight, opaque containers and storing them in cool, dark conditions helps maintain their quality and prevents nutrient loss over time.
Storage Duration: Over extended periods, even properly stored dehydrated red pepper may experience gradual degradation of some nutrients. Humidity, temperature fluctuations, and prolonged storage can affect both flavor and the stability of antioxidants. To maximize the health benefits, it is recommended to use dehydrated red pepper within its optimal shelf life, typically 12–24 months depending on packaging and storage conditions.

 English
English Français
Français Español
Español